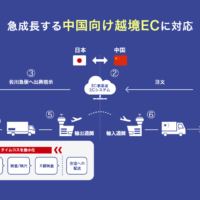
海外輸出ビジネスに興味があるが、どのように第一歩を踏み出せば良いか?
海外輸出ビジネスを始めるための第一歩は、輸出したい商品や市場に関する綿密なリサーチから始まります。
以下に、基本的なステップを挙げて説明します。
ただし、これらは一般的な情報であり、実際には各国の規制や市場状況、ビジネスの種類によって異なる場合があります。
1. 商品やサービスの選定:
– 市場ニーズを調査して、どの商品やサービスが海外で需要があるかを特定します。
2. ターゲット市場の選定:
– 潜在的な顧客がいる国や地域を特定し、その市場の特性や法規制、文化、消費者の嗜好などを理解します。
3. 輸出計画の作成:
– ビジネスプランを立て、輸出の目標、戦略、予算、リソース、リスク管理計画などを含めます。
4. 規制と要件の確認:
– 対象国の関税、税金、輸入規制などの法的要件を把握する必要があります。
5. ロジスティックスと配送:
– 国際物流のパートナーを見つけ、配送方法、費用、保険、追跡システムなどを確立します。
6. 輸出に必要な文書や許可の取得:
– 輸出する商品に応じて必要な許可証、健康証明書、原産地証明書などの文書を準備します。
7. 販売チャネルの構築:
– 海外代理店、ディストリビューター、卸売業者、またはオンラインプラットフォームを通じて販売チャネルを構築します。
8. マーケティングとプロモーション:
– 商品を市場に紹介し、ターゲット市場に合わせたマーケティング戦略を開発します。
9. 支払い方法と財務管理:
– 国際取引のための安全で信頼できる支払い方法を設定し、為替リスクの管理も含めます。
10. 継続的な市場調査と品質管理:
– 市場動向を常に監視し、商品の品質保持と顧客満足度の高いサービスを維持します。
これらのステップの根拠は、輸出業における成功の経験則、国際ビジネス教育プログラム、商業機関や政府による輸出ガイドライン、並びに輸出ビジネスのベストプラクティスから派生しています。
成功するためには、市場研究、計画、適切なパートナーシップ、実行力が重要とされています。
実際の経験を積むことが重要なため、初めは小規模から始めてビジネスの流れを学び、徐々に拡大していくことも一つの方法です。
継続的な学習と市場への適応は、国際ビジネスの不可欠な部分です。
輸出ビジネスに必要な資金はどのくらいで、資金調達にはどのような方法があるか?
輸出ビジネスを始めるにあたって、必要な資金はそのビジネスの規模、品目、市場選定、物流コストなどによって大きく異なります。
一般的に言えることは、次のような初期コストがかかる可能性があるということです。
1. 商品の仕入れや製造コスト
2. 国際輸送費用(海運、空輸など)
3. 保険費用
4. 輸出入関連の書類作成や手数料
5. 輸出入税・関税
6. 倉庫・保管費用
7. 市場調査およびマーケティング費用
8. 各国の法規制に適応するためのコンプライアンスコスト
9. 事業運営のための一般管理費(オフィス、スタッフの給料など)
資金調達の方法には、以下のような種類があります。
1. 自己資金:個人の貯蓄や既存事業からの利益など、手元にある資金を起業資金として使用します。
2. 銀行ローン:事業計画を基に金融機関から融資を受ける方法です。
返済能力が審査されます。
3. クラウドファンディング:プロジェクトや事業計画をインターネット上で紹介し、不特定多数から資金を集める方法です。
4. ベンチャーキャピタル:成長が見込まれるスタートアップ企業に投資するという方法で、大きな資金を確保できる場合があります。
5. エンジェル投資家:個人の投資家から資金を調達する方法で、エンジェル投資家は事業に積極的に関与する場合もあります。
6. 政府支援プログラム:多くの国では、中小企業の輸出を支援するための補助金や融資制度があります。
7. 製品先渡し販売(プレセール):製品が完成する前に販売を始め、その資金で生産や運輸を行う方法です。
具体的な資金の額については、業種や事業計画によって大きく異なり、十数万から数千万円単位の資金が必要になる場合もあります。
実際の資金調達については、ビジネスプランと資金調達先の条件を照らし合わせて検討する必要があります。
根拠としては、ビジネスプランや財務計画を通じて、事業の収益性、規模、成長性を示しながら、投資家や金融機関に説得力のある資料を提供することが重要です。
また、市場調査や業界分析を充分に行い、リスクを最小限に抑えることも投資家にとって魅力的なポイントとなります。
法規制や輸出手続きはどのように把握し、準備していくべきか?
海外輸出ビジネスを始める際には、様々な法規制や輸出手続きに注意を払う必要があります。
以下は、これらを把握し、準備するための基本的なステップです。
1. 製品や市場の調査:
最初に、どの製品をどの市場に輸出するかを決定し、その市場の輸入規制や消費者の嗜好を調査します。
2. 輸出規制の確認:
自国の輸出規制を確認します。
これには、輸出する製品が特定の許可やライセンスを必要としないか、または輸出禁止リストに含まれていないか確認することが含まれます。
3. 国際貿易法の理解:
国際貿易に関わる法律、特にWTO (世界貿易機関) のルール、地域的貿易協定、二国間の貿易合意などを熟知します。
4. 目的国の法規制の把握:
目的地の国の法律や規制を理解します。
これには、輸入関税、税金、特定の製品に対する輸入制限や基準、そして必要な標識やパッケージング要件が含まれます。
5. 貿易コンプライアンス:
自国と輸入国の法規制を遵守するために、弁護士や貿易コンサルタントに相談して適切な貿易コンプライアンスプログラムを確立します。
6. 輸出手続きの準備:
必要な輸出書類を準備します。
これには商業請求書、運送状(B/LまたはAWB)、原産地証明書、輸出免許証、梱包リストなどが含まれます。
7. 物流および運送会社の選定:
商品の輸出にあたっての物流や運送を管理するために、信頼できる運送会社やフォワーダーを選定します。
8. 融資と支払い条件の設定:
輸出入の支払い条件(信用状(L/C)、買取保証、前金など)を決定し、輸出のための融資手段を確保します。
9. 製品の品質管理:
目的国での安全基準や品質基準を満たしていることを保証するために、製品の品質管理プロセスを確立します。
10. リスク管理:
為替リスクや貿易リスク(政治的リスク、信用リスクなど)を評価し、保険でカバーするなどしてリスクマネジメントを行います。
根拠として、以下の機関の資料やウェブサイトが参考となります。
– 国税庁、財務省、経済産業省などの自国の政府機関
– 目的国の税関や政府関係のウェブサイト
– WTOや国際商工会議所(ICC)などの国際組織
常に最新の情報を入手するために、これらの組織から提供される公式なガイドラインやアップデートに注意を払うことが重要です。
また、地元の貿易関係団体や商業会議所といったネットワークを活用して情報収集や支援を受けるのも有効です。
輸出ビジネスの販路はどこにするべきか?
輸出ビジネスで販路を構築する際は、以下のポイントを考慮して戦略を立てる必要があります。
1. 市場リサーチ:
まずは、製品やサービスが求められている海外の市場を調査します。
どの国や地域がターゲットか、消費者のニーズや嗜好、現地の法規制、競合の状況などを綿密に分析する必要があります。
この情報は、市場選定の根拠となります。
2. 貿易協定と規制:
自国と輸出対象国との間の貿易協定や関税、輸出入規制を調査します。
これにより、輸出コストを把握し、コスト効率の良い販路を選択できます。
3. ディストリビューションチャネルの選択:
直接輸出や代理店を通じた間接輸出、合弁事業などさまざまな流通経路があります。
それぞれのメリットとデメリットを理解し、製品の特性や自身のビジネスモデルに合うかどうかを検討します。
4. Eコマースの活用:
オンライン販売は、少ない初期投資で広い範囲に販売できるため、スタートアップに適しています。
Amazonのような大手マーケットプレイスの利用や自社のオンラインショップの立ち上げなどが考えられます。
5. 展示会や見本市の活用:
業界の展示会や見本市に出展することで、多くのバイヤーや代理店と直接コンタクトを取れます。
ここでは、自社の製品を宣伝し、販路を拡大するチャンスがあります。
6. ネットワーキング:
業界団体への参加やビジネスネットワークの構築を通じて、情報収集や販路開拓を行います。
また、国際貿易の専門家や経験豊富なビジネスメンターからのアドバイスを求めることも有益です。
7. ソーシャルメディアとデジタルマーケティング:
ソーシャルメディアプラットフォームや検索エンジン広告を活用することで、対象とする市場や顧客層にリーチできます。
オンライン上での可視性を高めることは、ブランド認知の向上につながります。
8. 地元の文化と慣習を理解する:
輸出先の国の言語、文化、社会的慣習を理解することは、成功するビジネス関係を築く上で不可欠です。
各ポイントにおける根拠は、成功している輸出ビジネスの事例や、貿易に関する研究から導かれたベストプラクティスに基づいています。
市場調査やコンセンサスデータは根拠の厚い情報源であり、決定を下す際に利用されるべきです。
自社の製品やサービスに最適な販路を選択するには、これらの情報を総合的に分析し、戦略的な計画を立てる必要があります。
また、地道なネットワーキングやパートナーシップの構築も、販路開拓には重要です。